Plastic as a production material
Plastics are materials whose basic components are different polymers. The special structure of plastics makes it possible to adapt the technical properties by selecting the base material, manufacturing process and the addition of additives. As a result, the breaking strength, elasticity, hardness, temperature resistance, heat resistance and chemical resistance, for example, can be varied very well. Depending on their mechanical and thermal behavior, plastics are divided into thermoplastics, thermosets and elastomers.
Do you already know what material you need?
Then simply upload your finished data here. All files are automatically checked and optimized for production.
Order componentPlastics for selective laser sintering
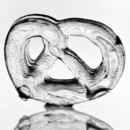
Polyamide plastics (PA), which are used in selective laser sintering, impress with their high mechanical strength and long-term stability. They are also resistant to numerous chemicals. Our materials are available in almost all colors, which you can easily select in the online configurator. We also manufacture media-tight components for special applications on request. In addition to a large selection of unfilled plastics, we also offer filled variants as well as flexible and particularly temperature-resistant materials. Thanks to our wide range of materials, we can find the right solution for every requirement.
Plastics for polyjet/multijet modeling
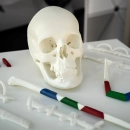
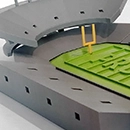
A wide range of materials is available for the PolyJet or MultiJet process. The combination of different resins creates composite materials with individual properties. Whether flexible like rubber or particularly stable - you can specify the desired material characteristics in the online configurator and receive a high-resolution 3D model according to your specifications. The liquid plastics enable the production of delicate components with a very smooth surface, which can also be easily reworked.
Plastics for stereolithography
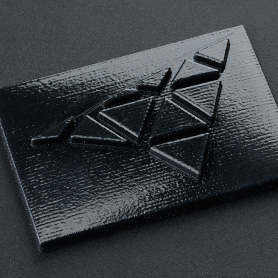
Epoxy resin components are characterized by a particularly fine reproduction of detail and a smooth, high-quality surface. Among other things, the stereolithography process is used for production: liquid resin is cured layer by layer using a UV laser. The VisiJet material variants "Tough", "Clear" and "HiTemp" are available, each with their own specific properties - from high load-bearing capacity and transparency to excellent temperature resistance.



 Deutsch
Deutsch English
English Italiano
Italiano