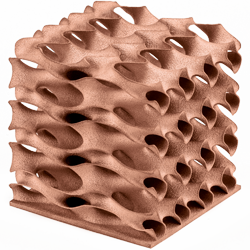
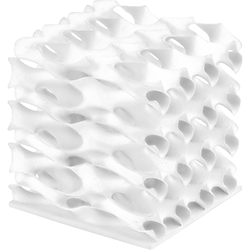
What is 3D printing?
Innovative technology with a wide range of applications
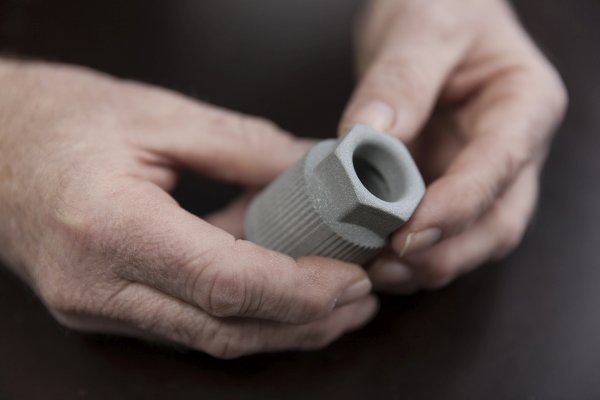
The term 3D printing summarizes all additive manufacturing processes in which three-dimensional components are produced layer by layer from a formless starting material. Originally, the technology mainly served to create prototypes directly from computer-generated 3D models as quickly as possible.
From niche technology to innovation engine
Since then 3D printing has established itself in numerous industries due to its seemingly unlimited capabilities. In addition to prototypes, which are still a relevant field of application for 3D printing today, industrial master forms and tool inserts made of plastic, metal or ceramic are produced using this technology. New materials are constantly being developed, increasing the potential areas of application for 3D printing.
3D printing service

3D objects for professional use
What requirements do you set for a service provider to whom you entrust the core of your company – your product? Do you expect high-precision results that can be used immediately? Do you prefer competent and expert advice from experienced experts?
Easily configured, simply ordered, delivered quickly
The PROTIQ Marketplace offers all that. Together with our reliable partners in industrial 3D printing, we provide you with outstanding expertise in the field of additive manufacturing. Based on our many years of experience with industry customers, we will advise and support you, from the generation of 3D data to the finished prototype, model or component. You will always receive the best service for your needs on the PROTIQ Marketplace.
3D printing processes
Plastic, metal, ceramics – the right technology for every material
The PROTIQ Marketplace offers 3D printing in many well-known processes. A wide range of high-quality materials lets us find the right solution for every customer requirement. For example, we provide you with reliable, functional components through selective laser sintering or detailed plastic prototypes that can be produced very quickly using stereolithography.
All 3D printing processes of the PROTIQ Marketplace
Selective laser melting (SLM)
Selective laser melting creates 3D metal objects. As in selective laser sintering, the powdery material is applied to the build platform by a squeegee or roller and locally fused by a laser. The high-power laser generates temperatures of up to 1,250 °C in the laser focus. To prevent workpieces from warping during production, they are firmly welded to the building board with a support structure.
.png)
Selective laser sintering (SLS)
The raw powder material is applied thinly to a build platform using a squeegee or roller. The laser melts the material according to the geometry specified by a CAD file. As a result, the build platform lowers by one layer thickness and the process repeats until the 3D object is complete. During the manufacturing process the temperature in the construction chamber lies just under the melting temperature of the material, which allows a particularly energy-efficient use of the laser.
Multi Jet Fusion
A powder-based process that works without any laser radiation: Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) wets the powder with two different binder liquids and fuses it almost simultaneously with the heat energy of several infrared lamps. In this way, versatile 3D plastic objects are created within a very short time.
Stereolithography (SLA)
The stereolithography 3D printing process creates a three-dimensional object layer by layer from a photosensitive plastic. This is done by irradiating liquid photopolymers (for example epoxy resin) with UV light. The resulting polymerization ensures local hardening of the material. The method allows the highest detail with wall thicknesses from 0.1 mm.
PolyJet/MultiJet modeling (PJM/MJM)
Similar to the traditional inkjet printer, PolyJet/MultiJet Modeling dispenses thin-film liquid plastic via an inkjet printhead. The acrylic or epoxy resins used are applied in layer thicknesses of 16-32 μm on a building platform and hardened with UV lamps.
Lithography-based Ceramic Manufacturing (LCM)
The LCM process is a multi-stage 3D printing process for processing technical ceramics. Initially, a green body is built up layer by layer with a liquid ceramic monomer suspension. The polymers are then removed from it by thermal debinding. Finally, the ceramic particles are compacted by a sintering process.
3D printing material
Plastic, Metal or Ceramic? At the PROTIQ Marketplace, you can choose the optimal material for your project from a wide range of basic materials and material combinations. We are constantly expanding our range of materials with innovative new developments. If you do not find a desired material in our assortment, please contact us personally!
3D printing with metal
Selective laser melting produces 3D metal objects that are dimensionally stable and durable. They are suitable for industrial applications that place high demands on mechanical durability and temperature resistance. Stainless steel, tool steel, aluminum, Inconel, CobaltChrom, and copper are available for your projects at the PROTIQ Marketplace.

3D printing with plastic
Plastics shine in 3D printing with incomparable material diversity and flexibility. Polyamide (PA) based plastics are predominantly used in selective laser sintering. 3D objects made of this thermoplastic, semi-crystalline material can be mechanically strong, resistant to most chemicals, and long-term stable. Liquid plastics used in PolyJet modeling or stereolithography can create transparent or multicolored components.
3D printing with ceramics
Ceramic materials used in 3D printing are characterized by their unique temperature resistance. The most widely used material, aluminum oxide, is resistant to temperatures over 1,000 °C. Its low weight and high end-product wear resistance make ceramics an attractive material for industrial use.
3D printing areas of application
We look at Additive Manufacturing every day in a new light
This puts us in a position to offer you hitherto unimagined possibilities with new materials and in-house developments in the areas of plant engineering and software. One example of our innovative strength is the development of high-conductivity copper, which now enables the application of 3D printing to many exciting areas, for example in the electronics industry or in the metalworking industry.
We actively shape the future of additive manufacturing
To accomplish this, we are constantly developing our processes and work closely with partners from research and development. Your advantage: You can extend your range of applications with new materials now and use the convenient features of the PROTIQ Marketplace to optimally support your processes.
3D printing models
3D printing offers you unrivaled creative freedom.
If your 3D model is to print successfully, however, it must meet certain requirements. We will explain to you common mistakes in 3D printing files and how to avoid them. On the PROTIQ Marketplace pages you will also find all the important information about which CAD programs you can use to create printable 3D models and where you can already purchase ready-made models.



 Deutsch
Deutsch English
English Italiano
Italiano



































.png)
.png)
.png)