3D File Formats in Comparison
Similar to graphics and audio files, 3D data can also be saved in numerous file formats. In addition to compatibility with common software, the decisive question here is what information the file should contain.One 3D is not like the other: What are the Differences?
In simple handling with 3D files, the question of the right format arises less frequently. Many programs for creating 3D data use their own file formats and specify their use directly, but also allow conversion to other formats.
However, in the professional use and industrial processing of 3D files - especially in additive manufacturing - users are regularly confronted with the differences that individual file formats have. This can get complicated especially when the file is to be sent for planning and production.
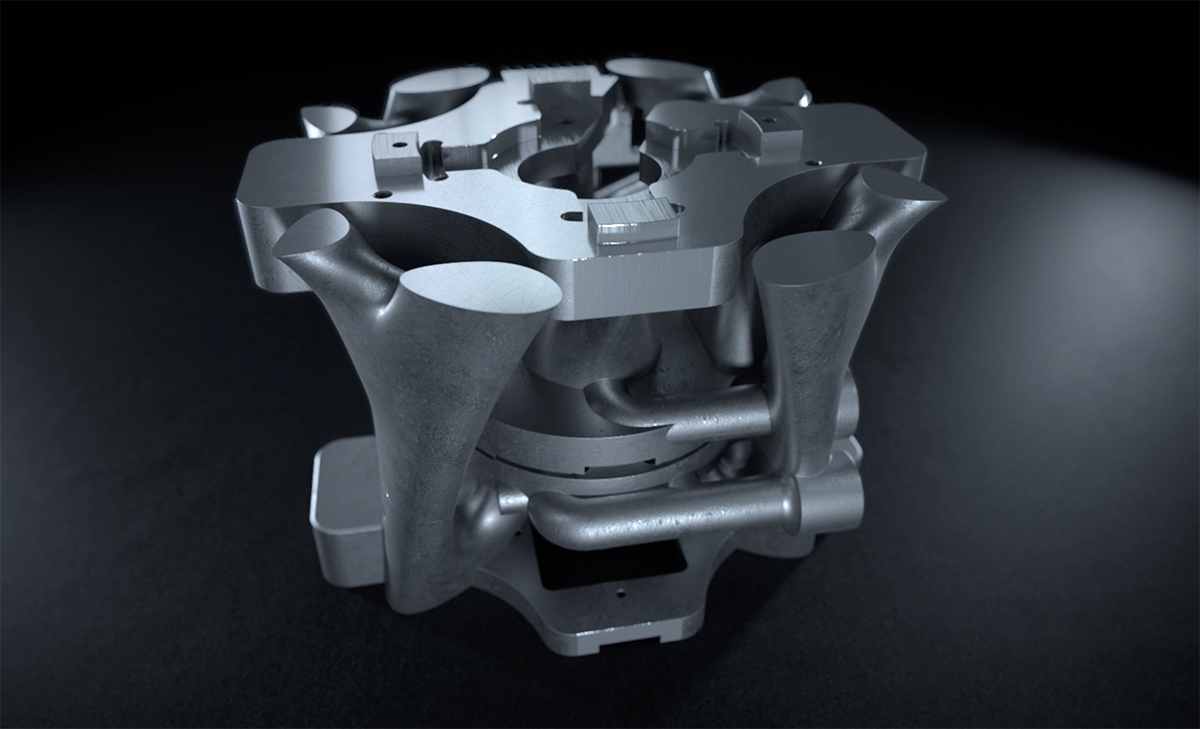
Differences of 3D File Formats
PROTIQ Marketplace is particularly diverse when it comes to 3D printing: In addition to the most common standard formats STL and OBJ, we process numerous other file formats, such as 3DM, 3DS, ACIS, VRML, ZPR, PLY, DXF, AMF, Sketch-Up, CATIA V4, CATIA V5, IGES, VDA, ProE, UG/ Parasolid, STEP, ACIS SAT, SolidWorks, JT, VDA, FBX and Collada.
We print your 3D objects- The 3D file format used affects the extent to which information about the printed material is included.
- The color or texture of the object to be produced can also be stored in some formats.
- Objects rendered in 3D files differ in their structure. Thus - depending on the format - high resolutions and delicate representations are limited.
- Internal information around the processing of the files can also be included in the saved data.



 Deutsch
Deutsch English
English Italiano
Italiano